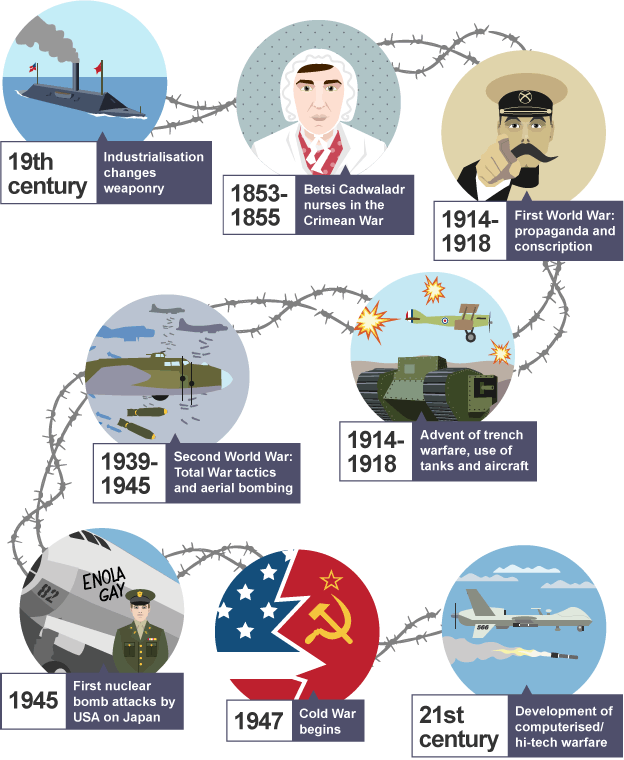
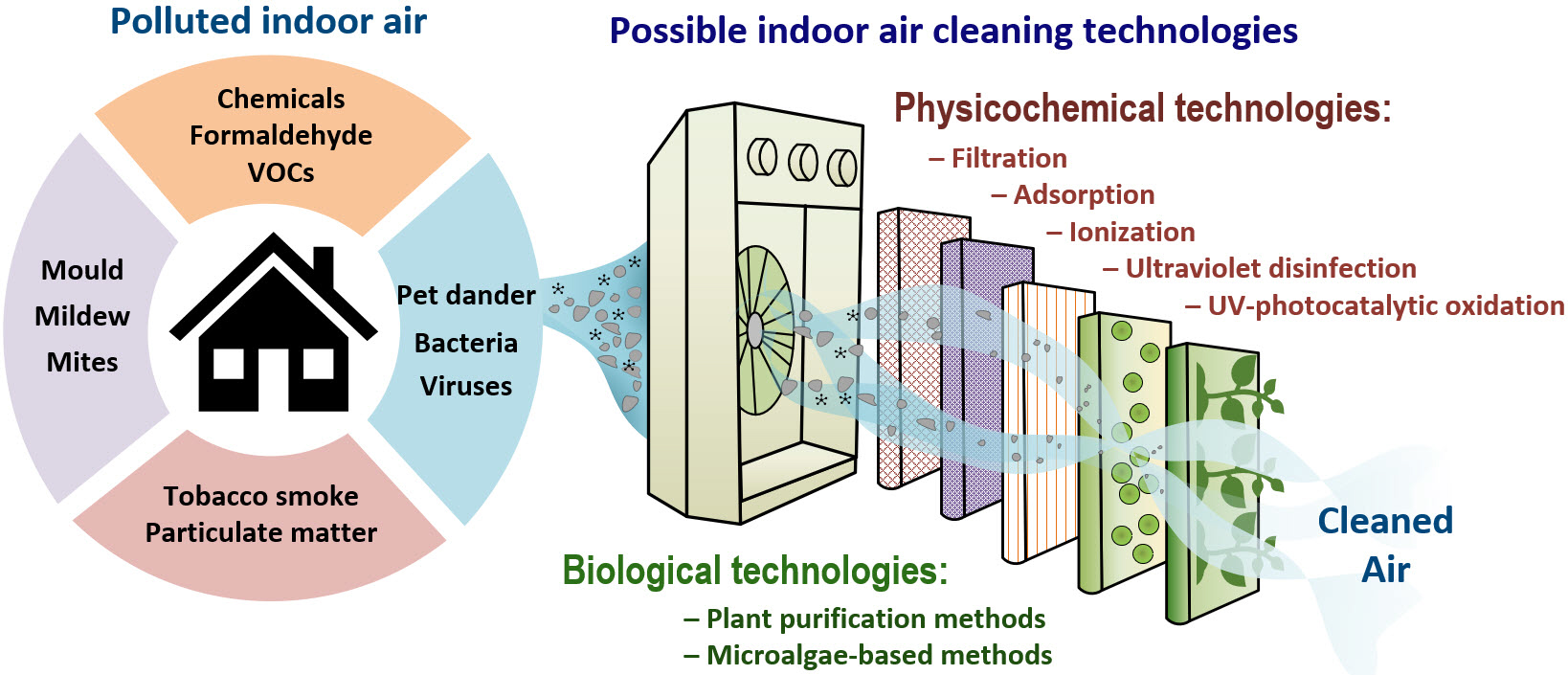
In the dawn of the 21st century, the digital landscape was vastly different from the intricate web of connections it has become today. The internet was primarily a repository of information, a burgeoning platform for e-commerce, and a burgeoning field for social interaction. However, as the digital ecosystem has evolved, so too have the threats that seek to exploit it. This evolution has necessitated a parallel transformation in digital defense mechanisms, from rudimentary antivirus software to sophisticated cybersecurity frameworks that protect against a diverse range of digital threats.
The early 2000s saw the rise of viruses and worms, simple yet effective malicious software that could cripple personal computers and entire networks. Defense mechanisms were largely reactive during this era, focusing on identifying and removing malware after it had infected a system. Antivirus software became a staple for digital users, employing signature-based detection to identify known threats. However, as attackers grew more sophisticated, relying solely on signature-based detection became akin to fighting the last war, always one step behind the innovators of malicious software.
The mid-2000s marked a significant shift in the nature of digital threats. Cybercriminals began exploiting vulnerabilities in software and operating systems to gain unauthorized access to data and systems. This era saw the rise of zero-day exploits, where attackers would take advantage of previously unknown vulnerabilities, leaving defenders scrambling to patch systems before significant damage could occur. In response, digital defense mechanisms began to incorporate proactive strategies, such as vulnerability assessments and penetration testing, to identify and rectify weaknesses before they could be exploited.
As the digital landscape continued to evolve, so too did the sophistication of threats. The late 2000s and early 2010s witnessed the emergence of advanced persistent threats (APTs), highly sophisticated and targeted attacks often sponsored by nation-states or large criminal organizations. APTs represented a significant escalation in the cyber threat landscape, capable of bypassing traditional security measures and remaining undetected for extended periods. This era demanded a more nuanced approach to digital defense, emphasizing threat intelligence, network segmentation, and behavioral analysis to detect and mitigate these complex threats.
The proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT) and the advent of cloud computing introduced new challenges and vulnerabilities. The increasing interconnectedness of devices and the shift towards storing and processing data off-premises required a reevaluation of digital defense strategies. Encryption, secure access protocols, and comprehensive endpoint security became critical components of a robust defense mechanism. Additionally, the concept of zero trust architecture began to gain traction, advocating for a security model that assumes no entity, whether inside or outside the network, should be automatically trusted.
In this complex and ever-evolving threat landscape, the role of cyber security services has become increasingly pivotal. These services offer a range of solutions tailored to the unique needs of organizations, encompassing risk assessments, managed security services, incident response, and compliance management. By leveraging expertise and cutting-edge technology, cyber security services play a crucial role in bolstering the digital defenses of organizations, ensuring they are equipped to navigate the myriad threats that characterize the digital age. These services offer a range of solutions tailored to the unique needs of organizations, encompassing risk assessments, managed security services, incident response, and compliance management. By leveraging expertise and cutting-edge technology, cybersecurity services play a crucial role in bolstering the digital defenses of organizations, ensuring they are equipped to navigate the myriad threats that characterize the digital age.
The current era of digital defense mechanisms is defined by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). These technologies offer the promise of predictive security, where systems can not only detect but also predict potential threats based on vast amounts of data and learning algorithms. AI and ML are transforming digital defense, enabling real-time threat detection, automated response, and adaptive security policies that evolve with the threat landscape. This represents a significant leap forward in the quest to stay ahead of attackers, offering a dynamic and proactive defense posture.
Looking to the future, the evolution of digital defense mechanisms will likely continue at an accelerated pace, driven by the relentless advancement of technology and the ingenuity of cybercriminals. Quantum computing presents both an opportunity and a challenge, with the potential to revolutionize encryption and data security while also posing a significant threat to current cryptographic standards. As we venture further into the 21st century, the digital defense mechanisms of tomorrow will need to be even more adaptive, intelligent, and integrated, capable of anticipating and neutralizing threats in a digital ecosystem that is increasingly complex and interconnected.
In conclusion, the evolution of digital defense mechanisms in the 21st century is a testament to the dynamic nature of the digital domain. From the reactive strategies of the early 2000s to the predictive capabilities of AI and ML today, digital defense has transformed dramatically in response to the evolving threat landscape. As we look ahead, the continued innovation and adaptation of digital defense mechanisms will be critical in securing the digital frontier against the ever-changing threats that seek to exploit it. The journey from simple antivirus software to sophisticated cybersecurity frameworks underscores the perpetual arms race between cyber defenders and attackers, a race that is set to continue as the stakes and the scope of the digital domain continue to expand.